
Heavy and prolonged menstrual bleeding, debilitating cramps that disrupt daily life, and most concerning of all—difficulty conceiving despite trying for a long time. If these symptoms sound familiar, they may indicate adenomyosis, a common yet often overlooked cause of female infertility. Today, advanced diagnostic and treatment options can help women regain their quality of life and significantly improve their chances of conception.
Heavy and prolonged menstrual bleeding, debilitating cramps that disrupt daily life, and most concerning of all—difficulty conceiving despite trying for a long time. If these symptoms sound familiar, they may indicate adenomyosis, a common yet often overlooked cause of female infertility. Today, advanced diagnostic and treatment options can help women regain their quality of life and significantly improve their chances of conception.
What Is Adenomyosis?
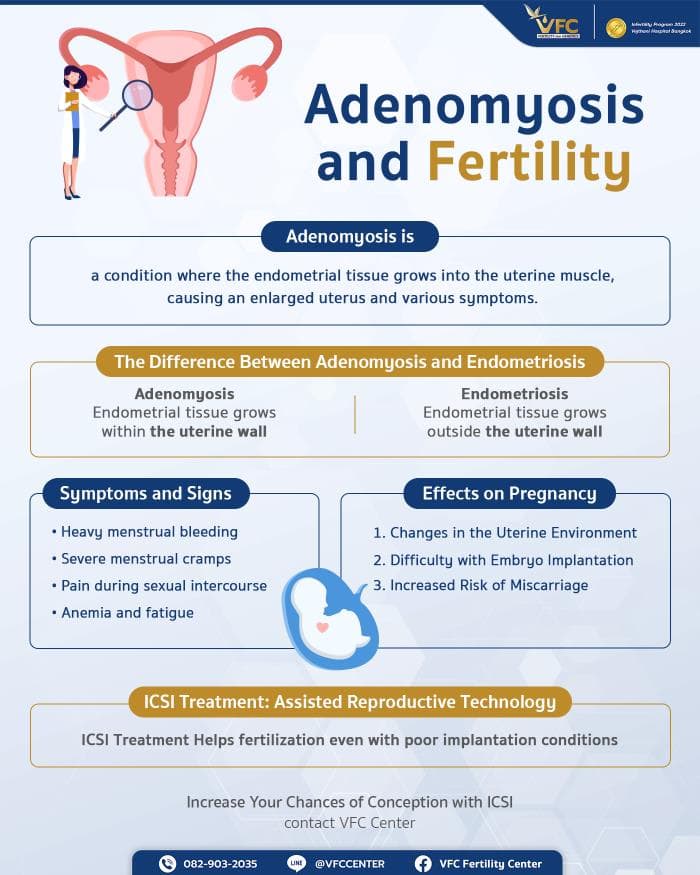
Adenomyosis is a condition where the endometrial tissue—the lining of the uterus—grows into the muscular wall of the uterus (myometrium). Normally, this tissue should only exist within the uterine cavity. When it invades the muscle layer, it causes the uterus to enlarge and leads to a variety of symptoms.
There are two main types of adenomyosis:
- Focal Adenomyosis: localized to a specific area.
- Diffuse Adenomyosis: widespread throughout the uterine wall.
Adenomyosis vs. Endometriosis: What’s the Difference?
Many people confuse adenomyosis with endometriosis. While both involve abnormal growth of endometrial tissue, they occur in different locations. Endometriosis refers to the growth of this tissue outside the uterus, such as on the ovaries or within the abdominal cavity. In contrast, adenomyosis is the growth of endometrial tissue within the uterine wall itself.
Signs and Symptoms of Adenomyosis
- Heavy and prolonged menstrual bleeding (menorrhagia) is the most common symptom of adenomyosis. Patients often need to change sanitary pads every 1–2 hours and may pass large blood clots.
- Severe menstrual cramps (dysmenorrhea) which may begin before menstruation and persist afterwards.
- Pain during intercourse (dyspareunia) which can strain intimate relationships.
- Anemia and chronic fatigue caused by prolonged heavy periods.
Impact on Fertility: Increased Risk of Infertility and Miscarriage
Adenomyosis can significantly affect fertility. The altered uterine environment can hinder embryo implantation and increase the risk of miscarriage. These complications make early diagnosis and proper treatment essential for women trying to conceive.
What Causes Adenomyosis?
Although the exact cause of adenomyosis remains unclear, two primary factors are believed to be involved:
- Hormonal influence, particularly estrogen: Elevated estrogen levels may encourage endometrial tissue to grow abnormally. In addition, uterine wall injury from surgical procedures—such as cesarean section or dilation and curettage—may create pathways for the tissue to invade the muscle layer.
- Genetic predisposition: Women with a family history of adenomyosis may have a higher risk of developing the condition themselves.
Who’s at Risk?
The primary risk group includes women aged 30 to 50, especially those who have given birth. Childbirth may cause microtrauma or scarring in the uterine wall, which can facilitate the abnormal growth of endometrial tissue into the muscle layer.
Adenomyosis Is Diagnosed
Diagnosis of adenomyosis typically involves several steps:
- Medical history and physical exam – Your physician will ask detailed questions about your menstrual cycle, the severity of pain, and any fertility challenges, followed by a pelvic examination.
- Ultrasound imaging – This is the initial tool used to assess uterine size and detect early changes in the uterine wall.
- MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging) – Offers clearer, more precise imaging than ultrasound, helping to distinguish adenomyosis from other uterine conditions and assess its severity.
- Blood tests – To check for anemia caused by chronic blood loss and to monitor relevant biomarkers.
- Differential diagnosis – It’s important to distinguish adenomyosis from other conditions such as fibroids or endometriosis to ensure appropriate treatment.
Adenomyosis and Fertility: Impact and Treatment Options
Adenomyosis can affect natural conception at various stages. Abnormal tissue growth alters the uterine environment, making it more difficult for an embryo to implant. Additionally, the abnormal muscle contractions in the uterus can increase the risk of miscarriage.
For couples struggling to conceive and dealing with adenomyosis, preparing for assisted reproductive technology is crucial since medical treatment to manage symptoms and reduce inflammation can help optimize the uterine environment before attempting fertility procedures.
Intracytoplasmic Sperm Injection (ICSI) is a common option in these cases. Because success rates may be lower in women with adenomyosis, close monitoring and a tailored treatment plan are essential to improving outcomes.
Prevention and Self-Care Tips
While adenomyosis cannot be completely prevented, lifestyle choices can help reduce symptom severity and improve overall reproductive health:
- Regular exercise – Promotes blood circulation and reduces inflammation. Light aerobic activities are especially beneficial for uterine health.
- Stress management – Techniques such as meditation, yoga, or deep relaxation can help reduce stress-induced hormonal imbalances.
- Anti-inflammatory diet – Include omega-3-rich fish, leafy greens, and fresh, colorful fruits to support hormone regulation and reduce inflammation.
- Avoid estrogen stimulants – Limit intake of red meat and avoid endocrine-disrupting chemicals that can promote endometrial tissue growth.
- Regular medical checkups – Ongoing evaluations allow physicians to monitor the condition and adjust treatment as needed, helping ensure more effective symptom control.
If you’re experiencing heavy, prolonged periods, severe menstrual cramps, or trouble conceiving, it may be time to investigate further. At VFC Center (V Fertility Center), we offer a full range of fertility treatments—including ICSI, IUI, egg freezing, and infertility screening in bangkok—tailored to your needs. Contact us to schedule a consultation and explore the best path forward for your reproductive health.
Article by Dr. Worawat Siripoon
Contact or Book a Consultation:
VFC Center – V-Fertility Center
Hotline: 082-903-2035
LINE Official: @vfccenter

OBSTETRICS AND GYNAECOLOGY-REPRODUCTIVE MEDICINE





No Comments
Sorry, the comment form is closed at this time.